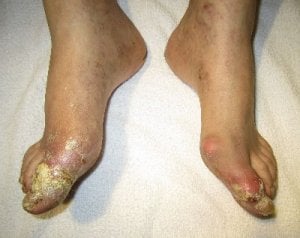
I used to think that foods high in uric acid were the most important aspect of managing gout diet.
I first published my list of foods high in uric acid on July 22nd, 2007. It took a lot of research to bring the science of purines into one list, and it’s been copied by thousands of websites around the world. At the time, after 2+ years working on this site, I knew more about gout than most people. A fraction of what I know now.
TL;DR
See Foods High in Uric Acid Chart summary.
I soon learned that purine control was not as important as many people suggested. You should never ignore purines from animal flesh. But there are other factors in diet that are more important. I’ve created a better Purine Rich Foods list that focuses on foods that really matter. You can still read my original high purine foods list below.
Foods High in Uric Acid Chart Review
During 2022, I am reviewing this page. With a view to reorganizing how I present information about gout foods. So after you have read this page, I hope that you will share with me:
- What brought you to this page?
- What information did you hope to read?
- How much did this page provide what you needed?
I have repeated the review link in the Feedback Section. So that you can easily share your thoughts after you have read this page. Thank you.
Foods High in Uric Acid
Please note that my explanations about purines after the chart are important. Because it is impossible to plan an effective gout diet if you only consider th purine content of your food intake.
If you just want help now, it is best to ask your doctor for dietary advice that supports your uric acid treatment plan. However, you might be unsure how to start such a consultation. In which case, please see your feedback options below to ask for help.
Foods High In Uric Acid Chart
If you feel that it is important to manage foods high in uric acid, then you should measure your total intake. Multiply the weight of your food (in grams) by the value from the table and divide this by 100 to give your uric acid intake in milligrams. In this way, you can calculate a total intake from the list of foods high in uric acid for every meal. You can compare purine intake totals with your blood test results to measure how food is affecting your uric acid levels.
|
Foods High in Uric Acid To find a particular food quickly, use your browser Find function (usually Ctrl-F). |
|
| Food | Purines (Uric Acid mg/100g) |
Very High Purine Foods (over 300 mg per 100 g) |
|
| Theobromine | 2300 |
| Yeast, Brewer’s | 1810 |
| Neck sweet bread, Calf’s | 1260 |
| Sprat, smoked | 804 |
| Sheep’s spleen | 773 |
| Yeast, Baker’s | 680 |
| Ox liver | 554 |
| Pig’s heart | 530 |
| Pig’s spleen | 516 |
| Pig’s liver | 515 |
| Also see Is Pork High in Purines? | |
| Mushroom, flat, edible Boletus, dried | 488 |
| Fish, sardines in oil | 480 |
| Liver, Calf’s | 460 |
| Ox spleen | 444 |
| Pig’s lungs (lights) | 434 |
| Ox lungs (lights) | 399 |
| Fish, sardine, pilchard | 345 |
| Spleen, Calf’s | 343 |
| Pig’s kidney | 334 |
High Purine Foods (200 to 300 mg per 100 g) |
|
| Fish, trout | 297 |
| Fish, Tuna in oil | 290 |
| Ox kidney | 269 |
| Fish, Tuna | 257 |
| Ox heart | 256 |
| Liver, chicken | 243 |
| Fish, Redfish (ocean perch) | 241 |
| Heart, Sheep’s | 241 |
| Fish, Anchovy | 239 |
| Black gram (mungo bean), seed, dry. Note: this is Vigna Mungo, which is not the same as black bean or mung bean. | 222 |
| Fish, Herring, Matje cured | 219 |
| Kidney, Calf’s | 218 |
| Fish, Herring, Atlantic | 210 |
| Horse meat | 200 |
Medium Purine Foods (100 to 200 mg per 100 g) |
|
| Bean, Soya, seed, dry | 190 |
| Fish, Herring roe | 190 |
| Lamb (muscles only) | 182 |
| Fish, Halibut | 178 |
| Chicken (breast with skin) | 175 |
| Veal, muscles only | 172 |
| Fish, salmon | 170 |
| Poppy seed, seed, dry | 170 |
| Pork muscles only | 166 |
| Also see Is Pork a Medium Purine Food? | |
| Goose | 165 |
| Sausage, liver (liverwurst) | 165 |
| Fish, Saithe (coalfish) | 163 |
| Fish, Carp | 160 |
| Ox tongue | 160 |
| Pork leg (hind leg) | 160 |
| Chicken, boiling fowl, average | 159 |
| Pork fillet | 150 |
| Pork shoulder with skin (blade of shoulder) | 150 |
| Turkey, young animal, average, with skin | 150 |
| Veal knuckle with bone | 150 |
| Veal, leg of veal with bone | 150 |
| Veal, neck with bone | 150 |
| Lungs, Calf’s | 147 |
| Shrimp, brown | 147 |
| Fish, Mackerel | 145 |
| Pork chop with bone | 145 |
| Caviar (real) | 144 |
| Sunflower seed, dry | 143 |
| Pike | 140 |
| Pork chuck | 140 |
| Veal chop, cutlet with bone | 140 |
| Veal fillet | 140 |
| Veal, shoulder | 140 |
| Fish, Haddock | 139 |
| Duck, average | 138 |
| Venison haunch (leg) | 138 |
| Pig’s tongue | 136 |
| Scallop | 136 |
| Beef, muscles only | 133 |
| Rabbit meat, average with bone | 132 |
| Fish, Sole | 131 |
| Ham, cooked | 131 |
| Bean, seed, white, dry | 128 |
| Lentil, seed, dry | 127 |
| Pork belly, raw, smoked dried | 127 |
| Beef, chuck | 120 |
| Beef, fore rib, entrecote | 120 |
| Pork hip bone (hind leg) | 120 |
| Lobster | 118 |
| Chicken (chicken for roasting), average | 115 |
| Mussel | 112 |
| Sausage “Jagdwurst” | 112 |
| Beef, fillet | 110 |
| Beef, roast beef, sirloin | 110 |
| Beef, shoulder | 110 |
| Chicken, leg with skin, without bone | 110 |
| Fish, Pike-perch | 110 |
| Fish, Cod | 109 |
| Peas, chick (garbanzo), seed, dry | 109 |
| Grape, dried, raisin, sultana | 107 |
| Linseed | 105 |
| Rabbit/Hare (average) | 105 |
| Venison back | 105 |
| Sausage salami, German | 104 |
| Sausages, frying, from pork | 101 |
| More Moderate Purine Foods | 100-200 |
Low Purine Foods (50 to 100 mg per 100 g) |
|
| Pork belly | 100 |
| Also see Is Pork Low in Purines? | |
| Barley without husk, whole grain | 96 |
| Sausage “Mortadella” | 96 |
| Pea, seed, dry | 95 |
| Oats, without husk, whole grain | 94 |
| Plaice | 93 |
| Brain, Calf’s | 92 |
| Mushroom, flat, edible Boletus, cep | 92 |
| Sausages, frying, from veal | 91 |
| Oyster | 90 |
| Frankfurter sausages | 89 |
| Sausage “Bierschincken” | 85 |
| Pea, pod and seed, green | 84 |
| Pig’s brain | 83 |
| Broccoli | 81 |
| Bean sprouts, Soya | 80 |
| Tench | 80 |
| Nuts, peanut | 79 |
| Artichoke | 78 |
| Fish, eel (smoked) | 78 |
| Sausage “Fleischwurst” | 78 |
| Sausage, Vienna | 78 |
| Ox brain | 75 |
| Leek | 74 |
| Sausages, German (Mettwurst) | 74 |
| Apricot | 73 |
| Sausage “Munich Weisswurst” | 73 |
| Cocoa powder, oil partially removed, not including theobromine | 71 |
| Grass, Viper’s (black salsify) | 71 |
| Meat, luncheon | 70 |
| Brussel sprouts | 69 |
| Tofu | 68 |
| Chives | 67 |
| Fig (dried) | 64 |
| Plum, dried | 64 |
| Millet, shucked corn | 62 |
| Sesame (gingelly) seed, Oriental, dry | 62 |
| Fish, Crayfish | 60 |
| Crispbread | 60 |
| Mushroom | 58 |
| Banana | 57 |
| Beef, corned (German) | 57 |
| Parsley, leaf | 57 |
| Spinach | 57 |
| Peppers, green | 55 |
| Pudding, black | 55 |
| Corn, sweet | 52 |
| Cauliflower | 51 |
| Rye, whole grain | 51 |
| Wheat, whole grain | 51 |
| More Low Purine Foods | 50-100 |
Very Low Purine Foods (below 50 mg per 100 g) |
|
| Oyster, mushroom | 50 |
| Kale | 48 |
| Beans, French, dried | 45 |
| Pumpkin | 44 |
| Pasta made with egg (noodles, macaroni, spaghetti, etc. | 40 |
| Lettuce, Lamb’s | 38 |
| Almond, sweet | 37 |
| Beans, French (string beans, haricot) | 37 |
| Cabbage, savoy | 37 |
| Nuts, hazelnut (cobnut) | 37 |
| Date, dried | 35 |
| Elderberry, black | 33 |
| Melon, Cantelope | 33 |
| Cabbage, red | 32 |
| Cheese, Limburger, 20% fat content in dry matter | 32 |
| Celeriac | 30 |
| Morel | 30 |
| Quince | 30 |
| Bamboo Shoots | 29 |
| Mushrooms, canned, solid and liquid | 29 |
| Olive, green, marinated | 29 |
| Cress | 28 |
| Grape | 27 |
| Kohlrabi | 25 |
| Nuts, Walnut | 25 |
| Plum | 24 |
| Squash, summer | 24 |
| Asparagus | 23 |
| Nuts, Brazil | 23 |
| Bilberry, blueberry, huckleberry | 22 |
| Cabbage, white | 22 |
| Aubergine | 21 |
| Chinese leaves | 21 |
| Peach | 21 |
| Rolls, bread | 21 |
| Strawberry | 21 |
| Avocado | 19 |
| Beet root | 19 |
| Kiwi fruit (Chinese gooseberry, strawberry peach) | 19 |
| Orange | 19 |
| Pineapple | 19 |
| Caviar substitute | 18 |
| Potato, cooked with skin | 18 |
| Raspberry | 18 |
| Carrot | 17 |
| Cherry, Morello | 17 |
| Currant, red | 17 |
| Endive | 17 |
| Mushrooms, Chanterelle | 17 |
| Mushrooms, Chanterelles, canned, solids & liquids | 17 |
| Gooseberry | 16 |
| Potato | 16 |
| Sauerkraut, dripped off | 16 |
| Radish | 15 |
| Apple | 14 |
| Beer, real, light | 14 |
| Bread, wheat (flour) or (white bread) | 14 |
| Fennel leaves | 14 |
| Beer, Pilsner lager beer, regular beer, German | 13 |
| Lettuce | 13 |
| Onion | 13 |
| Radishes | 13 |
| Chicory | 12 |
| Pear | 12 |
| Rhubarb | 12 |
| Tomato | 11 |
| Cheese, cottage | 9.4 |
| Beer, alcohol free | 8.1 |
| Yogurt, min. 3.5% fat content | 8.1 |
| Cucumber | 7.3 |
| Cheese, Brie | 7.1 |
| Cheese, edam, 30% fat content in dry matter | 7.1 |
| Cheese, edam, 40% fat content in dry matter | 7.1 |
| Cheese, edam, 45% fat content in dry matter | 7.1 |
| Cherry, sweet | 7.1 |
| Cheese, Cheddar/Cheshire cheese, 50% fat content in dry matter | 6 |
| More Very Low Purine Foods | 0-50 |
You can see that my purines table shows actual numbers. If you are unsure about purines and foods high in uric acid, please read How Purines Affect Gout.
I include purine data in my nutrition summary for gout food. So, to see your favorite uric acid food, ask me to add it to the gout & uric acid food list.
I took the data in this table from Food Composition and Nutrition Tables by Souci, Fachmann, Kraut. Their notes for the purine data states:
Purines
The total of free and bound compounds is given for each component. The “total purines” column contains the total of all individual components calculated as uric acid.
The exact calculation of this is beyond the scope of this article, but you can easily see the relative purine count in the table. Remember, the table of foods high in uric acid shows the number of milligrams per 100 grams, so intake will depend on portion size.
Beer and Gout Update
I’ve flagged this article, for review. Are you are interested in more information about beer for gout sufferers? Please share your questions, opinions, and experiences in the comments below.
Healthy Foods High in Uric Acid
Thanks for reading my foods high in uric acid chart. Please stop worrying about purines now, and start worrying about your health. The simple truth is this:
If the amount of animal purines in your diet is high enough to significantly affect your uric acid level, then you have an unhealthy diet.
You have choices:
- Bore yourself stupid with a low purine diet that you’ll never stick to, and won’t change your gout
- Confuse yourself with avoiding all sorts of different foods and never get a good diet
- Move towards a well-balanced diet that will improve your general health and give you the best chance of treating your gout successfully
I’ll help you with whichever choice you make, though I obviously recommend option 3. Some vegetarian diets, alkalizing diets, or Mediterranean style diets can be very good for gout when planned and managed properly. Please remember that, just as with any uric acid lowering treatment, dietary gout controls must be managed properly. So your best approach is to agree a healthy eating plan with a qualified health professional. Then you might work with your doctor to switch some high-purine meats and fish for lower purine choices. In a way that helps you and your doctor achieve your safe uric acid target. But also be sure to arrange adequate pain control for the months that it takes to get uric acid safe.
If you have had gout long enough to notice it, then you have uric acid deposits throughout your body. Some of these may cause gout attacks as they dissolve. You might avoid this if you are lucky, but for most people, a low uric acid diet is going to hurt before it gets better.
I understand every aspect of this, and I want to help you make the right choices. As you and your doctor work together to control your gout. It’s a serious matter, and I have a seriously good gout forum. In that forum you can get learn how other gout sufferers have managed foods high in uric acid.

Foods High in Uric Acid & Purines
Foods high in uric acid affect every gout sufferer differently. Some gout sufferers need to control uric acid food intake carefully. Others need to focus on different dangers in food and drink. I’ve added links at the end of the article where you can get personal help for foods high in uric acid.
Actually, food never contains uric acid, it contains something called purines, and your body converts purines to uric acid.
This is important! Because excess uric acid is what causes gout.
I have 2 surprises for you about purines.
Foods High in Uric Acid Surprises
The first surprise about high uric acid foods is: vegetable purines are not important!
Yes, that’s right! Vegetable purines do not increase uric acid in our bodies, and they can be ignored. You might need to be careful with foods high in animal purines, but there is no evidence to show that foods high in vegetable purines will increase uric acid.
I have updated the foods high in uric acid table with my Purine Rich Foods chart to only show animal purines that affect gout. You can still see the original foods high in uric acid chart below.
The second surprise is: though eating animal purines can raise your uric acid level, it has no immediate effects on gout attacks. That’s right – high purine meals do not cause gout attacks! However, they can raise the risk of gout attacks over several months. The latest science shows that it is a different food component that triggers gout flares. You will not get any immediate gout flare reduction from reducing purine intake, and you can only measure results of purine changes by getting your blood tested for uric acid.
Foods High In Uric Acid Explanation
Dietitians and nutritionists commonly measure foods high in uric acid by measuring the total purine content of food.
The table below lists foods high in uric acid first with purine concentration reducing as you move down the list. Many advisers tell gout sufferers to avoid anything over 400 mg and restrict foods in the 100-400 mg range, but you should treat this advice with caution.
Firstly, you must realize that typical portion sizes vary enormously.
Be sure to calculate the amount that applies to your typical serving size from the value shown for 100 grams.
Secondly, the effect of foods high in uric acid depends on absorption of purines through the digestive tract. Most uric acid derives from the breakdown of your cells as part of normal metabolism. The overall contribution of foods varies from person to person. Different gout studies report figures of between 5% and 15%.
Purines Warning
Please be careful about getting obsessed with the purine content of food. Though purines in food can have an effect on uric acid, there are many other factors to consider. Read more about the main food factors that can affect gout in the Gout Diet section.
More Help for Foods High In Uric Acid
I recommend you do not take this type of food list too seriously. Firstly, gout food research indicates that vegetable purines do not increase the risk of gout, and dairy foods can actually reduce it. More importantly, people digest foods differently – a food that causes gout in one person might be tolerated by another, and different food combinations have significantly different effects.
You have learned that you can stop worrying about vegetable purines. You also know that animal purines only increase the long-term risk of gout attacks, with no immediate attacks on gout flares. New information changes the way gout should be managed. Science tells us that gout diet must be managed on a personal basis, and total food intake is far more important than a few individual foods or drinks.
I can help you understand how foods high in uric acid affect Your gout. First I help you collect important facts that you can keep in your own personal gout profile. Then I provide several places where you can discuss your gout facts to get the right gout diet for you.
What do you want to do next to learn about how foods high in uric acid affect your gout?
Get personal help now, using the forum link below, or read more gout diet facts.
Purine control used to be considered the best way to manage your gout diet. But we now know that it is a waste of time to simply avoid high purine foods. Unless we consider types of purine, and other diet factors. Let me help you make the most important diet choices for gout.
I'm working on templates that help you identify, understand, and resolve your concerns about foods high in uric acid. In the meantime, you can start by adding notes about what you've learned about foods high in uric acid so far.
All you do is highlight any text that interests you. Then click "Annotations" to personalize any GoutPal page. Which means you can keep your foods high in uric acid notes linked here, where you can always find them.
Do you need help with annotations? Or other unanswered questions or unresolved concerns? Then please ask in the Gout Forum. Or, if you prefer to use email, then subscribe to my free newsletter.
Leave Foods High In Uric Acid to browse Gout Diet Guidelines. Or return to Gout Progression Phase 5: Start Uric Acid Cure.
Foods High In Uric Acid Related Topics
Please remember: to find more related pages that are relevant to you, use the search box near the top of every page.
Common Terms: beef, broccoli, cabbage, fish, fruit, halibut, lettuce, meat, Most Helpful Gout Pages, olive, pickle, pork, pumpkin, salmon, squash, trigger, uric diet
Other posts that include these terms:
- High Alkaline Foods for Gout Diet Menu
- Gout Foods Table for Vegetables
- Gout Food List for GoutPal Foodies
- Gout Foods Table for Meat
- Purine Rich Foods
- Does Alcohol Affect Gout?
- Colchicine For Gout
- What Foods Cause Gout?
- Is Chinese Food Bad For Gout?
- Is Very Low Purine Gout Diet Possible?
- Edamame and Gout: Vegetable Medley
- Gout Symptoms, Causes, & Diagnosis
- Fish You Can Eat With Gout
- Gout Foods Tables Introduction
- Best Drink For Gout – What’s Yours?
- Is Crawfish Bad for Gout?
- Gout and Alcohol: Tequila and Gout
- Is Pork High in Purines?
- Gout Medications To Avoid Gout By Lower Uric Acid
- What Gout Foods Can I Eat?
- Gout Snacks – Which Foods are Best?
Please give your feedback
Did this page help you? If yes, please consider a small donation. Your donations help keep GoutPal's gout support services free for everyone.
If not, please tell me how I can improve it to help you more.
TL;DR - Foods High in Uric Acid Chart
Food does not contain uric acid. Uric acid forms from purines in meat, fish, and our own flesh.
Vegetable purines do not increase uric acid.
Excess food is a bigger risk than purines because it leads to more uric acid from human flesh.
Total daily and weekly diet control in a balanced diet is more important than avoiding certain foods.