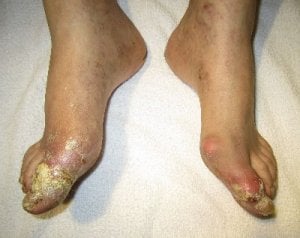
Cinnamon cassia oil for gout is not a recognized treatment. However, there is some evidence to show that it will lower uric acid.
To date, it has only been tested on mice. Therefore, you must exercise caution when considering cinnamon cassia oil as a gout home remedy. Though many people consider home remedies to be safer natural options to pharmaceutical treatments, that is rarely true. Pharmaceuticals must pass rigorous safety testing prior to launch, yet herbal remedies can be sold with no safety tests. There is also a question about dosing, but before I consider that, let me introduce the report that prompted this article.
Cinnamon Cassia Oil for Gout Report
This is my layman’s summary of the abstract of:
- Title:
- Effects of cassia oil on serum and hepatic uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activities in mouse liver.
- Authors:
- Zhao X, Zhu JX, Mo SF, Pan Y, Kong LD.
- Published:
- J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Feb 20;103(3):357-65.
Xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) and xanthine oxidase (XO) are the enzymes responsible for converting purines into uric acid. Allopurinol reduces uric acid production by inhibiting these enzymes, which are normally produced in the liver.
Hepatic means related to the liver.
Oxonate-induced mice are mice that have had uric acid levels artificially induced by injecting with potassium oxonate. This is a widely used method for inducing gout in lab test animals by inhibiting uricase which would otherwise cause uric acid to be converted to harmless allantoin.
Cinnamon Cassia Oil for Gout Report Abstract
This is an investigation into the uric acid lowering effects of cassia oil taken by mouth. The oil was extracted from Cinnamomum cassia. Tests were performed on mice with artificially raised uric acid. The investigators tested for reduced liver xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) and xanthine oxidase (XOD) activities.
Various doses were given to mice, divided into different groups with control groups. Uric acid was lowered in the blood and in the liver according to dose. Uric acid of mice given doses of 450 mg/kg of cassia oil or above returned to the same level as normal control mice. At 600 mg/kg, cassia oil was as potent as allopurinol, and reduced uric acid in the liver to lower than normal. In normal mice, cassia oil lowered uric acid in the liver, but not in blood. Cassia oil significantly reduced the measured liver enzymes, though not as much as allopurinol.
These results suggested that uric acid lowering effects of cassia oil could be explained, at least partly, by inhibiting those liver enzymes responsible for converting purines to uric acid.

Cinnamon Cassia Oil for Gout Dosing
There is a great deal of difficulty when extrapolating doses from animal experiments to humans. At its simplest level, FDA recommendations are to multiply mouse dose per kg by 3 to get the Human Equivalent Dose (HED). HED is measured by surface area, and the average male is just under 2 m2. Taking the effective doses from this investigation (450 to 600 mg), we get human dose of 1350 mg to 1800 mg.
Unfortunately, there is no readily available information on the safety of this level of dosing. Medscape tells us that 1000 to 6000 mg is safe, but only for up to 4 months. We then have the problem of determining the strength of cassia oil. As this is largely unregulated, it is almost impossible to know exactly what dose of the active ingredient you are actually taking.
By all means, discuss the potential of cassia oil for gout with your doctor. I cannot recommend it, but if your doctors can explain its safety profile, then please share their advice with your fellow gout sufferers in the gout forum.
Leave Cinnamon Cassia Oil for Gout to read more Gout Treatment pages.
Please give your feedback
Did this page help you? If yes, please consider a small donation. Your donations help keep GoutPal's gout support services free for everyone.
If not, please tell me how I can improve it to help you more.
- YouTube
- The gout forums.